User Management
FortiAuthenticator’s user database has the benefit of being able to associate extensive information with each user, as you would expect of RADIUS and LDAP servers. This information includes whether the user is an administrator, uses RADIUS authentication, or uses two-factor authentication, and includes personal information such as full name, address, password recovery options, and the groups that the user belongs to.
The RADIUS server on the FortiAuthenticator unit is configured using default settings. For a user to authenticate using RADIUS, the option Allow RADIUS Authentication must be selected for that user’s entry, and the FortiGate unit must be added to the authentication client list. See RADIUS service on page 1.
This section includes the following subsections:
- Administrators
- Local Users
- Remote Users
- Remote user sync rules
- Social Login Users
- Guest Users
- User groups
- Usage Profile
- Organizations
- Realms
- FortiTokens
- MAC Devices
Administrators
Administrator accounts on FortiAuthenticator are standard user accounts that are flagged as administrators. Both local users and remote LDAP users can be administrators.
Once flagged as an administrator, a user account’s administrator privileges can be set to either full access or customized to select their administrator rights for different parts of the FortiAuthenticator unit.
The subnets from which administrators are able to log in can be restricted by entering the IP addresses and netmasks of trusted management subnets.
There are log events for administrator configuration activities. Administrators can also be configured to authenticate to the local system using two-factor authentication.
An account marked as an administrator can be used for RADIUS authentication if Allow RADIUS Authentication is selected. See RADIUS service on page 1. These administrator accounts only support Password Authentication Protocol (PAP).
See Configuring a user as an administrator for more information.
Local Users
Local user accounts can be created, imported, exported, edited, and deleted as needed. Expired local user accounts can be purged manually or automatically (see General).
To manage local user accounts, go to Authentication > User Management > Local Users.
The local user account list shows the following information:
| Create New | Select to create a new user. |
| Import | Select to import local user accounts from a CSV file or FortiGate configuration file. If using a CSV file, it must have one record per line, with the following format: user name (30 characters max), first name (30 characters max), last name (30 characters max), email address (75 characters max), mobile number (25 characters max), password (optional, 128 characters max). If the optional password is left out of the import file, the user will be emailed temporary login credentials and requested to configure a new password. Note: Even if an optional field is empty, it still must be defined with a comma. |
| Export Users | Select to export the user account list to a CSV file. |
| Disabled Users | Purge Disabled: This offers the option to choose which type of disabled users to purge. All users matching the type(s) selection will be deleted. Re-enable: This allows the administrator to re-enable disabled accounts. Expired users accounts can only be re-enabled individually. |
| Edit | Select to edit the selected user account. |
| Delete | Select to delete the selected user account or accounts. |
| Search | Enter a search term in the search field, then select Search to search the user account list. |
| Username | The user accounts’ usernames. |
| First name | The user accounts’ first names, if included. |
| Last name | The user accounts’ last names, if included. |
| Email address | The user accounts’ email addresses, if included. |
| Admin | If the user account is set as an administrator, a green circle with a check mark is shown. |
| Status | If the user account is enabled, a green circle with a check mark is shown. |
| Token | The token that is assigned to that user account. Select the token name to edit the FortiToken, see FortiToken device maintenance. |
| Groups | The group or groups to which the user account belongs. |
| Authentication Method | The authentication method used for the user account. |
| Expiration | The date and time that the user account expires, if an expiration date and time have been set for the account. |
Adding a user
When creating a user account, there are three ways to handle the password:
- The administrator assigns a password immediately and communicates it to the user.
- The FortiAuthenticator unit creates a random password and automatically emails it to the new user.
- No password is assigned because only token-based authentication will be used.
To add a new user:
- In the local users list, select Create New. The Create New User window opens.
- Enter the following information:
- Select OK to create the new user.
You will be redirected to the Change user window to continue the user configuration.
If the password creation method was set to No password, FortiToken authentication only you will be required to associate a FortiToken with the user before the user can be enabled. See FortiAuthenticator and FortiTokens.
Editing a user
User accounts can be edited at any time. When creating a new user, you will be immediately redirected to the Change user window to complete the user configuration.
To view the Change user window, go to the user account list, select the user you will be editing, and then select Edit from the toolbar. Conversely, selecting the username in the user list will also open the Change user window.
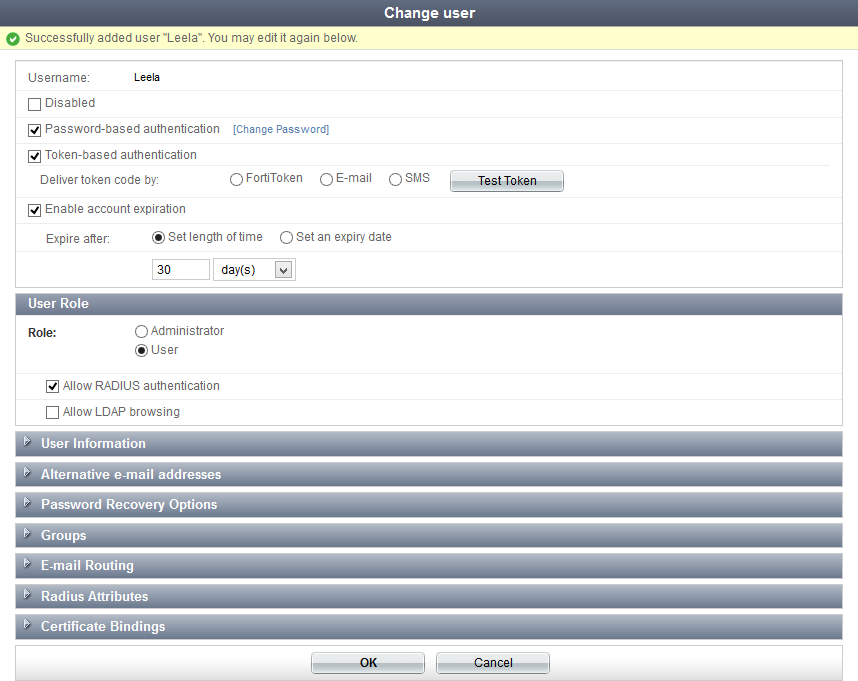
The following information can be viewed or configured:
| Username | The user’s username. This cannot be changed. | |
| Disabled | Select to disable the user account. | |
| Password-based authentication | Select to enable password based authentication. Select Change Password to open the Change password window, where you can change the user’s password. |
|
| Token-based authentication | Select to enable FortiToken based authentication. See Configuring token based authentication. | |
| Enable account expiration | Select to enable account expiration. See Enable account expiration. | |
| User Role | Configure the user’s role. | |
| Role | Select Administrator or User. If setting a user as an administrator, see Configuring a user as an administrator. |
|
| Allow RADIUS authentication | Select to allow RADIUS authentication. This applies only to non-administrator users. | |
| Allow LDAP browsing | Select to Allow LDAP browsing. This applies only to non-administrator users. | |
| User Information | Enter user information, such as their address and phone number. See Adding user information. | |
| Alternative e-mail addresses | Add alternate email addresses for the user. | |
| Password Recovery Options | Configure password recovery options for the user. See Configuring password recovery options | |
| Groups | Assign the user to one or more groups. See User groups. | |
| E-mail Routing | Enter a mail host and routing address into their respective fields to configure email routing for the user. | |
| Radius Attributes | Add RADIUS attributes. See RADIUS Attributes. | |
| Certificate Bindings | Add, edit, or removed certificate bindings for the user account. See Configuring certificate bindings. Select the certificate name to view the certificate, or select the Revoke Certificate button to revoke the certificate. |
|
Select OK when you have finished editing the user’s information and settings.
Configuring token based authentication
Token-based authentication requires one of the following:
- a FortiToken device or mobile device with the FortiToken Mobile app installed,
- a device with either email or SMS capability.
If a FortiToken device or FortiToken Mobile app will be used, it must first be registered in Authentication > User Management > FortiTokens. See FortiTokens for more information.
To configure an account for token-based authentication:
- Go to the Change user window for the requisite user account.
- Select Token-based authentication to view the token-based authentication options.
- Do one of the following:
- Select FortiToken, then select the FortiToken device serial number from the FortiToken Hardware or FortiToken Mobile drop-down lists, as appropriate.
- Select Email and enter the user’s email address in the User Information section.
- Select SMS and enter the user’s mobile number in the User Information section.
- Select Test Token to validate the token passcode. The Test Email Token or Test SMS Token window opens (depending on your selection).
- For email and SMS tokens, confirm that the contact information is correct, select Next, then enter the token code received via email or SMS.
- Select Back to return to edit the contact information, select Verify to verify the token passcode, or select Resend Code if a new code is required.
- For FortiToken, enter the token code in the Token code field, then select Verify to verify the token passcode.
- Select OK.
The device must be known to the FortiAuthenticator unit. See FortiToken devices and mobile apps.
Optionally, select Configure a temporary e-mail/SMS token to receive a temporary token code via email or SMS.
|
|
By default, token-based authentication must be completed within 60 seconds after the token passcode is sent by email or SMS. To change this timeout, go to Authentication > User Account Polices > General and modify the Email/SMS Token Timeout field, see Lockouts. |
Configuring a user as an administrator
See Administrators for more information.
To set a user as an administrator:
- Go to the Change user window for the requisite user account.
- In the User Role section, select Administrator for the Role.
- In the Access field, select Full to give the administrator fill administrative privileges, or select Custom to customize the administrator’s permissions.
- Optionally, select Web service access to allow the administrator to access the web services via a REST API or FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows.
- Select Restrict admin login from trusted management subnets only, then enter the IP addresses and netmasks of trusted management subnets in the table, to restrict the subnets from which an administrator can log in.
- Select OK to apply the changes to the user.
If Custom is selected, find the permissions that the user will have in the Available user permissions list, and move them to the Selected user permissions list.
Adding user information
User information can be added in the Change user window. Some information can be required depending on how the user is configured. For example, is the user is using token-based authentication by SMS, then a mobile number and SMS gateway must be configured before the user can be enabled.
The following user information can be entered:
| First name | Last name |
| Email address | Phone number |
| Mobile number | SMS gateway: select from the drop-down list. Select Test SMS to send a test message. |
| Street address | |
| City | State/Province |
| Country: Select from the drop-down list. | |
| Language: select a specific language from the drop-down list, or use the default language. | |
| Organization: select an organization from the drop-down list. See Organizations. | |
| Max. devices: Select either Use global configuration, or Specify a custom number. | |
| User has: The number of device the user currently has. | |
| Custom user fields: See Custom User Fields for more information. | |
Configuring password recovery options
To replace a lost or forgotten password, the FortiAuthenticator unit can send the user a password recovery link by email or in a browser in response to a pre-arranged security question. The user then must set a new password.
To configure password recovery by email:
- Go to the Change user window for the requisite user account.
- Ensure that the user has an email address entered. See Adding user information.
- In the Password Recovery Options section, Select E-mail recovery.
- Optionally, select Alternative e-mail addresses and enter additional email addresses for this user.
- Select OK to apply the changes.
In the event of password recovery, an email message will be sent to all configured email addresses — both the user information email address and the alternative email addresses.
To configure password recovery by security question:
- Go to the Change user window for the requisite user account.
- In the Password Recovery Options section, select Security question, then select Edit. The Setup a Security Question dialog box opens.
- Choose one of the questions in the list, or select Write my own question and enter a question in the Custom question field.
- Enter the answer for the question in the Answer field.
- Select OK to create the security question.
- Select OK in the Change user window to apply your changes.
How the user can configure password recovery by security question:
- Log in to the user account. The View Profile page opens.
- Select Edit Profile at the top left of the page.
- In the Password Recovery Options section, select Security Question, and select Edit.
- Choose one of the questions in the list, or select Write my own question and enter a question in the Custom question field.
- Enter the answer for your question.
- Select OK.
How the user can configure password recovery by email:
- Log in to the user account. The View Profile page opens.
- Select Edit Profile at the top left of the page.
- In the Password Recovery Options section, select E-mail recovery.
- Optionally, select Alternative e-mail addresses and enter additional email addresses for this user.
- Select OK.
How the user recovers from a lost password:
- Browse to the IP address of the FortiAuthenticator.
- At the login screen, select Forgot my password.
- Select either Username or Email as your method of recovery.
- Enter either your username or email address as selected in the previous step, and then select Next.
- Do one of the following:
- If an email address was entered, check your email, open the email and select the password recovery link.
- If a username was entered, answer the security question and then select Next.
- On the Reset Password page, enter and confirm a new password and then select Next.
Security policies must be in place on the FortiGate unit to allow these sessions to be established.
This information is used to select the user account. If your information does not match a user account, password recovery cannot be completed.
The recovery options available depend on the settings in the user account.
The user can now authenticate using the new password.
Configuring certificate bindings
To use a local certificate as part of authenticating a user, you need to:
- Create a user certificate for the user, see To create a new certificate:.
- Create a binding to that certificate in the user’s account.
To create a binding to a certificate in a user’s account:
- Go to the Change user window for the requisite user account.
- Expand the Certificate Bindings section.
- Select Add Binding. The Create New Local User Certificate Binding window opens.
- Select either Local CA or Trusted CA and then select the applicable CA certificate from the drop-down list.
- Enter the Common Name on the certificate. For example, if the certificate says
CN=rgreenthen enterrgreen. - Select OK to add the new binding.
Remote Users
Remote LDAP users must be imported into the FortiAuthenticator user database from LDAP servers, see LDAP on page 1.
|
|
Note that if you have an unlicensed version of FAC-VM you will only be able to import a maximum of five remote users. |
|
|
A FortiToken device already allocated to a local account cannot be allocated to an LDAP user as well; it must be a different FortiToken device. |
Remote RADIUS users can be created, migrated to LDAP users, edited, and deleted.
LDAP users
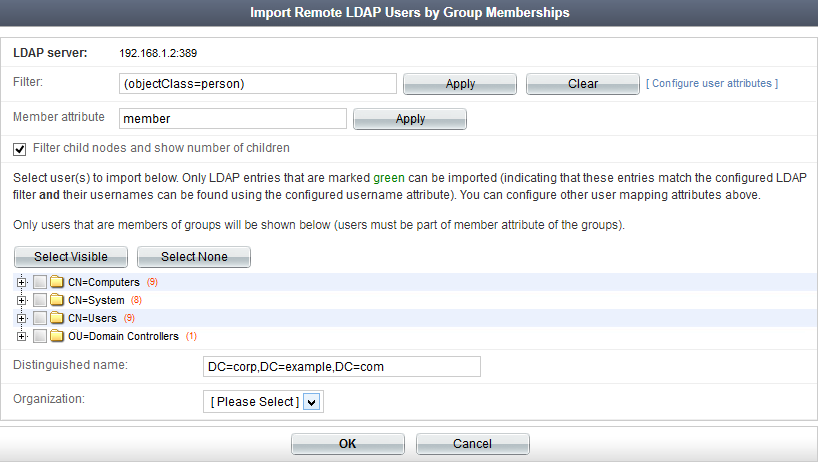
To import remote LDAP users:
- Go to Authentication > User Management > Remote Users, ensure that LDAP users is selected, then select Import. The Import Remote LDAP Users screen opens.
- Select a remote LDAP server from the Remote LDAP server drop-down list, select Import users or Import users by group membership, then select Go.
- Optionally, enter a Filter string to reduce the number of entries returned, and then select Apply, or select Clear to clear the filters.
|
|
An LDAP server must already be configured to select it in the drop-down list. See Remote authentication servers on page 1 for information on adding a remote LDAP server. |
The Import Remote LDAP Users or Import Remote LDAP Users by Group Memberships window opens in a new browser window.
|
|
Please note that the Member attribute field is only available if you select to Import users by group membership. Use this field to specify the filter by which users will be shown. In the example, the default attribute (member) will only show users that are members of groups (users must be part of member attribute of the groups). |
- The default configuration imports the attributes commonly associated with Microsoft Active Directory LDAP implementations. Select Configure user attributes to edit the remote LDAP user mapping attributes.
- Select the entries you want to import.
- Optionally, select an organization from the Organization drop-down to associated the imported users with a specific organization. See Organizations.
- Select OK.
Selecting the field, FirstName for example, presents a list of attributes which have been detected and can be selected. This list is not exhaustive and additional, non-displayed attributes may be available for import. Consult your LDAP administrator for a list of available attributes.
The amount of time required to import the remote users will vary depending on the number of users being imported.
To add two-factor authentication to a remote LDAP user:
- From the remote user list, select the user you are editing. The Edit Remote LDAP User window opens.
- Select Token-based authentication, then follow the same steps as when editing a local user (Editing a user).
- Configure the User Role, User Information, Radius Attributes, and Certificate Bindings for the user as needed.
- Select OK to apply the changes.
RADIUS users
To view remote RADIUS users, go to Authentication > User Management > Remote Users and select RADIUS users in the toolbar. See RADIUS on page 1 for more information about remote RADIUS servers.
The following options are available:
| Create New | Select to create a new remote RADIUS user. |
| Delete | Select to delete the selected user or users. |
| Edit | Select to edit the selected user. |
| Migrate | Select to migrate the selected user or users. See To migrate RADIUS users to LDAP users:. |
| Token-based Auth | Select to enforce or bypass token-based authentication for the selected user or users. |
| Search | Search the remote RADIUS user list. |
| Username | The remote user’s name. |
| Remote RADIUS server | The remote RADIUS server or which the user resides. |
| Token | The FortiToken used by the user, if applicable. |
| Enforce token-based authentication | Whether or not token-based authentication is enforced. |
To create a new remote RADIUS user:
- From the remote user list, select RADIUS users, then select Create New. The Create New Remote RADIUS User window opens.
- Enter the following information:
- FortiToken: select the FortiToken device serial number from the FortiToken Hardware or FortiToken Mobile drop-down lists, as appropriate.
- The device must be known to the FortiAuthenticator unit. See FortiToken devices and mobile apps.
- Optionally, select Configure a temporary e-mail/SMS token to receive a temporary token code via email or SMS.
- Email: enter the user’s email address in the User Information section.
- SMS: enter the user’s mobile number in the User Information section.
- Email address
- Mobile number and SMS gateway
- Language
- Organization - see Organizations.
- Select OK to create the new remote RADIUS user.
| Remote RADIUS | Select the remote RADIUS server on which the user will be created from the drop-down list. For more information on remote RADIUS servers, see RADIUS on page 1. | |
| Username | Enter a username. | |
| Enforce token-based authentication if configured below | Select to enforce the token-based authentication, if you are configuring token-based authentication. | |
| Token-based authentication | Select to configure token-based authentication. | |
| Deliver token code by | Select the method by which token code will be delivered. One of: |
|
| User Information | Enter user information as needed. The following options are available: |
|
To migrate RADIUS users to LDAP users:
- From the remote RADIUS users list (see Learned RADIUS users), select the user or users you need to migrate, then select Migrate from the toolbar. The Migrate RADIUS Users to LDAP Users window opens.
- Select a LDAP server from the drop down list to which the selected RADIUS user or users will be located, then select Next.
- Enter the distinguished names for the users that are being migrated, or browse the LDAP tree (see Directory tree overview on page 1) to find the users.
- Select Migrate to migrate the user or users.
Remote user sync rules
Synchronization rules can be created to control how and when remote users are synchronized. To view a list of the remote user synchronization rules, go to Authentication > User Management > Remote User Sync Rules.
To create a new remote user synchronization rule:
- From the Remote User Sync Rules page, select Create New. The Create New Remote User Synchronization Rule windows opens.
- Configure the following settings:
- Select OK to create the new synchronization rule.
| Name | Enter a name for the synchronization rule. |
| Remote LDAP | Select a remote LDAP server from the drop-down list. To configure a remote LDAP server, see Remote authentication servers on page 1. |
| Sync every | Select the amount of time between synchronizations. |
| Base distinguished name | Base DN of the remote LDAP server that automatically populates when a remote LDAP server is selected above. |
| LDAP filter | Optionally, enter an LDAP filter. Select Test Filter to test that the filter functions as expected. |
| Token-based authentication sync priorities | Select the required authentication synchronization priorities. Drag the priorities up and down in the list change the priority order. |
| Sync as | Select to synchronize as a remote user or as a local user. Selecting either option will open a pop-up dialog box displaying the user fields that will be synchronized for that selection. |
| Group to associate users with | Optionally, select a group from the drop-down list with which to associate the users with, or select Create New to create a new user group. See User groups. |
| Organization | Optionally, select an organization from the drop-down list with which to associate the users with, or select Create New to create a new organization. See Organizations. |
| Certificate binding CA |
Certificate binding CA for users who use remote user sync rules. When the Certificate binding common name field is populated (under LDAP User Mapping Attributes), this field must also be specified. |
| LDAP User Mapping Attributes | Optionally, edit the remote LDAP user mapping attributes. |
| Preview Mapping | Select to preview the LDAP user sync mappings in a new window. |
| Show Sync Fields | Select to view the user fields that will be synchronized. |
Social login users
Users who have authenticated and logged in through a social WiFi captive portal will appear here.
For more information on the various social captive portal methods available, see Social WiFi authentication.
Guest users
Guest user accounts can be created as needed. Guest users are similar to local users, only they are created with a restrictes set of attributes.
To manage guest user accounts, go to Authentication > User Management > Guest Users.
Users can be authenticated against local or remote user databases with single sign-on using client certificates or SSO (Kerberos/SAML).
Common use cases might include:
- Hotel receptionists creating room accounts
- Office staff creating visitor accounts
Newly created account information can be sent to user email, SMS, or printed out individually.
To create a new guest user/multiple guest users:
- Go to Authentication > User Management > Guest Users and select Create New. The Create New Guest User window opens.
- Enter the following information:
|
|
A new "Sponsor" role for local and remote users has been added in FAC version 5.0. This role is equivalent to an administrator with Read-Write permissions to the Guest Users sub-menu only, including a new built-in "Sponsor" permissions set. |
| General | ||
| Creation Mode |
There are three guest user creation methods:
|
|
| Expiry date | Determine the date that the guest user account/s will expire. | |
| Expiry time | Determine the time that the guest user account/s will expire. The time can either be manually entered, or defined from four options: Now, Midnight, 6 a.m., or Noon. | |
| Express | The following is only available when Creation Mode is set to Express. | |
| Number of new guest users | Number of new guest users to be added, up to a maximum of 1000. | |
| Groups | Choose user groups from the list available to assign the new guest users. | |
| CSV Import | The following is only available when Creation Mode is set to From CSV file. | |
| CSV file | Choose a CSV file to import the user attributes information from a CSV file. | |
| Guest Basic Information | The following is only available when Creation Mode is set to Manual Input. | |
| Add Guest User | Manually enter guest user information, including their First name, Last name, Email address, and Mobile number. Choose user groups from the list available to assign the new guest users. | |
User groups
Users can be assigned to groups during user account configuration (see Editing a user), or by editing the groups to add users to it.
To view the user groups list, go to Authentication > User Management > User Groups.
|
|
Note that, as of FortiAuthenticator 4.3, user groups can be created for MAC devices. However, MAC devices will only be available to add in a MAC user group once devices have been created or imported. To see how to do this, see MAC Devices. |
To create a new user group:
- Go to Authentication > User Management > User Groups and select Create New. The Create New User Group window opens.
- Enter the following information:
- Optionally, you may enable Allow token self-provisioning. For more details, see Token self-provisioning.
- Select OK to create the new group.
| Name | Enter a name for the group. |
| Type | Select the type of group: Local, Remote LDAP, Remote RADIUS, or MAC. |
| Users | Select users from the Available users box and move them to the Selected users box to add them to the group.
This option is only available if Type is Local. |
| User retrieval | Determine group membership by selecting either Specify an LDAP filter or Set a list of imported remote users. This option is only available if Type is Remote LDAP. |
| Remote LDAP | Select a remote LDAP server from the drop-down list. At least one remote LDAP server must already be configured, see Remote authentication servers on page 1. This option is only available if Type is Remote LDAP. |
| Remote RADIUS | Select a remote RADIUS server from the drop-down list. At least one remote RADIUS server must already be configured, see Remote authentication servers on page 1. This option is only available if Type is Remote RADIUS. |
| LDAP filter | Enter an LDAP filter. Optionally, select Test filter to ensure that the filter works as expected. This option is only available if Type is Remote LDAP and User retrieval is set to Specify an LDAP filter. |
| LDAP users | Select remote LDAP users from the Available LDAP users box and move them to the Selected LDAP users box to add them to the remote group. This option is only available if Type is Remote LDAP and User retrieval is set to Set a list of imported remote users. |
| RADIUS users | Select remote RADIUS users from the Available RADIUS users box and move them to the Selected RADIUS users box to add them to the remote group. This option is only available if Type is Remote RADIUS. |
To edit a user group:
- In the user group list, select the group that you need to edit.
- Edit the settings as required. The settings are the same as when creating a new group.
- Select OK to apply your changes.
User groups for MAC-based RADIUS authentication
Once created, MAC user groups can then be used under the MAC-based authentication section of RADIUS clients, under Authentication > RADIUS Service > Clients. See Clients for more information.
Usage profile
Usage profiles can be created to determine user time and data usage on a granular level.
To view the usage profile list, go to Authentication > User Management > Usage Profile.
To create a new usage profile:
- Go to Authentication > User Management > Usage Profile and select Create New. The Create New Usage Profile window opens.
- Enter the following information:
| Name | Enter a name for the profile. | |
| Description | Optionally, enter information about the usage profile. | |
| Time Usage | Select how time usage is determined. | |
| Time limit |
For this profile, the user's time limit will be either unlimited or measured from the moment their account was created, from when they first logged on, or how much time they have used. When the method has been chosen, enter the time period, in either minutes, hours, days, weeks, or months. The default is set to seven days. |
|
| Data Usage |
Select how data usage is determined. |
|
| Data limit |
For this profile, the user's data limit will either be unlimited or restricted to the amount of data they have used. If data usage is to be limited, enter the data amount in either KB, MB, GB, or TB. The default is set to 1 GB. |
|
| Time Schedule | Select the timezone the usage profile should follow. | |
| Timezone | Timezone the usage profile should follow. The default is set to (GMT) UTC - No Daylight Savings. | |
- Select OK to add the new usage profile.
Organizations
Organizations include a name and logo. An organization can be associated with local and remote users.
When a user provisions FortiToken Mobile on their device, the organization name and logo are automatically pushed to the device, allowing the FortiToken Mobile App’s user interface to be rebranded.
Organizations can be created, edited, and deleted as needed. Organization are applied to users from the various user management pages. See Local Users, Remote Users, and Remote user sync rules.
To manage organizations, go to Authentication > User Management > Organizations.
To create a new organization:
- From the organization list, select Create New to open the Create New Organization window.
- Enter a name for the organization in the Name field.
- Optionally, select Browse... to locate the logo image for the organization on your computer.
- Select OK to create the new organization.
|
|
The image can be a maximum of 320x320 pixels, and must be 24-bit, and in the .PNG format. |
Realms
Realms allow multiple domains to authenticate to a single FortiAuthenticator unit. They support both LDAP and RADIUS remote servers. Each RADIUS realm is associated with a name, such as a domain or company name, that is used during the log in process to indicate the remote (or local) authentication server on which the user resides.
For example, the username of the user PJFry, belonging to the company P_Express would become any of the following, depending on the selected format:
- PJFry@P_Express
- P_Express\PJFry
- P_Express/PJFry
The FortiAuthenticator uses the specified realm to identify the back-end RADIUS or LDAP authentication server or servers that are used to authenticate the user.
Acceptable realms can be configured on a per RADIUS server client basis when configured RADIUS service clients. See User Management.
To manage the realms, go to Authentication > User Management > Realms.
To create a new realm:
- From the realms list, select Create New. The Create New Realm window opens.
- Enter a name for the realm in the Name field.
- Select the user source for the realm from the User source drop-down list. The options include local users, or users from specific RADIUS or LDAP servers.
|
|
The realm name may only contain letters, numbers, periods, hyphens, and underscores. It cannot start with a special character. |
- Enable Chained token authentication with remote RADIUS server. Note that this option is only available when selecting a remote LDAP server as the User source.
|
|
FortiAuthenticator 4.3 now supports chained authentication, providing the ability to chain two different authentication methods together so that, for example, a two-factor authentication RSA solution can validate passcodes via RADIUS. |
- Select OK to create the new realm.
FortiTokens
Go to Authentication > User Management > FortiTokens to view a list of configured FortiTokens. From here, FortiTokens can be added, imported, exported, edited, deleted, and activated. For more information, see FortiToken devices and mobile apps.
The following information is shown:
| Create New | Create a new FortiToken, see To add FortiTokens manually:. |
| Import | Import a list of FortiTokens, see To import FortiTokens from a CSV file: and To import FortiTokens from a FortiGate unit:. |
| Export | Export the FortiToken list, see To export FortiTokens:. |
| Delete | Delete the selected FortiToken or FortiTokens. |
| Edit | Edit the selected FortiToken or FortiTokens. |
| Activate | Activate the selected FortiToken or FortiTokens. |
| Search | Enter a search term in the search field, then select Search to search the FortiToken list. |
| Serial number | The FortiToken’s serial number. |
| Token type | The FortiToken type, either FortiToken Hardware or FortiToken Mobile. |
| Status | Whether or not the FortiToken is activated. |
| Comment | Comments about the token. |
| User | The user to whom the FortiToken applies. |
| Size | The size of the token. |
| Drift | The time difference between the FortiAuthenticator and the FortiToken. For information on removing the drift, see FortiToken drift adjustment. |
| Timestep | The FortiToken timestep. |
| FTM License | The FTM license applied to the FortiToken. |
MAC Devices
Non-802.1X compliant devices can be identified and accepted onto the network using MAC address authentication. See Non-compliant devices for more information.
Go to Authentication > User Management > MAC Devices to view a list of configured MAC devices. From here, MAC devices can be created, imported, deleted, and edited.
The following information is shown:
| Create New | Create a new MAC-based authentication devices. |
| Import | Import a list of MAC devices from a CSV fileTo import FortiTokens from a CSV file: |
Once created/imported, MAC devices can be added to MAC user groups. See User groups for more information.
RADIUS Attributes
Some services can receive information about an authenticated user through RADIUS vendor-specific attributes. FortiAuthenticator user groups and user accounts can include RADIUS attributes for Fortinet and other vendors.
Attributes in user accounts can specify user-related information. For example, the Default attribute Framed-IP-Address specifies the VPN tunnel IP address to be sent to the user by the Fortinet SSL VPN.
Attributes in user groups can specify more general information, applicable to the whole group. For example, specifying third-party vendor attributes to a switch could enable administrative level login to all members of the Network_Admins group, or authorize the user to the correct privilege level on the system.
To add RADIUS attributes to a user or group:
- Go to Authentication > User Management > Local Users and select a user account to edit, or go to Authentication > User Management > User Groups and select a group to edit.
- In the RADIUS Attributes section, select Add Attribute. The Create New User Group RADIUS Attribute or Create New User RADIUS Attribute window opens.
- Select the appropriate Vendor and Attribute ID, then enter the attribute’s value in the Value field.
- Select OK to add the new attribute to the user or group.
- Repeat the above steps to add additional attributes as needed.
